Getting Started with Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in LabVIEW
LabVIEW is a great language. What could make it better? Objects.
Object-oriented programming adds a dimension to LabVIEW that can help bring order to your program and keep that order as it grows. If you have used OO in other languages, most of the principles are still in place. If it is a new concept, don't let that keep you from harnessing the power of objects to improve your LabVIEW code.
There is a learning curve, of course. But it is well worth it.
Object-oriented programming adds a dimension to LabVIEW that can help bring order to your program and keep that order as it grows. If you have used OO in other languages, most of the principles are still in place. If it is a new concept, don't let that keep you from harnessing the power of objects to improve your LabVIEW code.
There is a learning curve, of course. But it is well worth it.
Why use OOP?
|
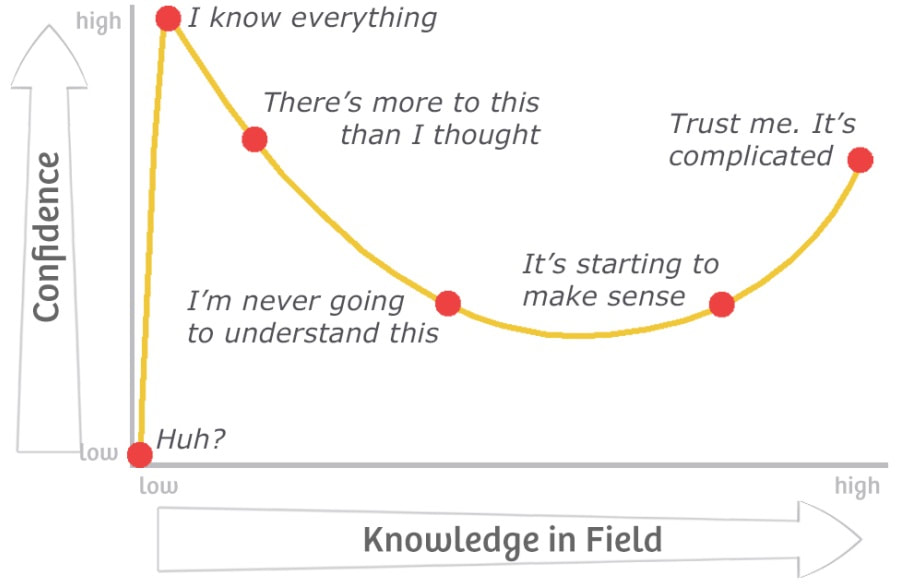
The Dunning-Kruger Effect
How learning something new works |
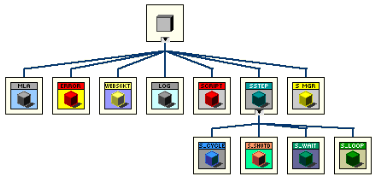
OO Basics
Encapsulation
|
Scoping / Access Privilege
|
Inheritance
Inheritance is a type of relationship between Parent & Child Classes. Child classes inherit attributes and functionality from their parents. From there, child classes can grow to include additional attributes and functionality that the parent does not possess.
Polymorphism
The word polymorphism comes from Latin, meaning “many forms”. This is the OO concept that there are varying forms of things that have similarities. For example, you may have multiple forms of shapes, such as Square, Circle, and Triangle, that have certain similarities, like color, size, and position.
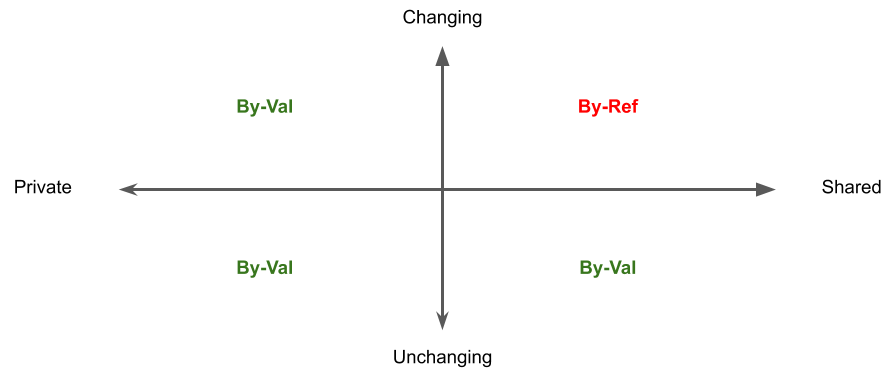
By Value vs. By Reference
There are two ways a program can manage an object in memory: by Value or by Reference.
|
By Value (By-Val)
|
By Reference (By-Ref)
|
So, how do you choose when to use By-Val or By-Ref?
The right choice depends on the purpose of the object and how it is used in the program.
The right choice depends on the purpose of the object and how it is used in the program.
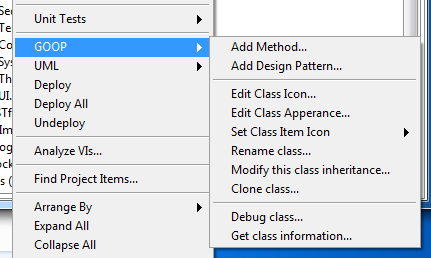
Helpful Tools
NI GDS (GOOP Development System)
- Available in VIPM
OpenGDS
- Available for download at opengds.github.io and github.com/opengds/OpenGDS